Technology has changed the way we travel. Smartphones, travellers' comments and photos, search engines and algorithms can all inspire and empower us to plan complex journeys all over the globe within minutes.
Planning and booking tourism has always had an element of risk. One has to commit upfront – there is no sample to try before you buy and no return policy. It is not surprising that people increasingly rely on social media content and networks to identify, evaluate and select their preferred tourism destination and suppliers.
But even if the final destination is beautiful, many social media users will now ask themselves a set of new questions. Is it the trendy and fashionable place that you want to be “seen” travelling? It this a place you won’t be embarrassed to share with your peers and followers online?
In TripAdvisor we trust
Increasingly, TripAdvisor is the starting point for information (photos, videos, comments, blogs) for choosing a travel destination, particularly among millennials.
Travel inspired by social media has gained popularity because it saves time and reduces the purchase risk of travellers when searching for travel information and planning their trip.
The universal penetration of smartphones has created the “always switched-on” tourists, who use their devices to share tourism experiences on the spot and in real time. Identifying, searching and sharing tourism experiences and information have been identified as the two top major ways in which social media has transformed tourism.
For many people, mobile phones have become their external brain when on the road. However, in some cases, continuous mobile phone use on holidays has led to tourists anthropomorphising their devices, by attributing them human characteristics and perceiving them as personal travel companions.
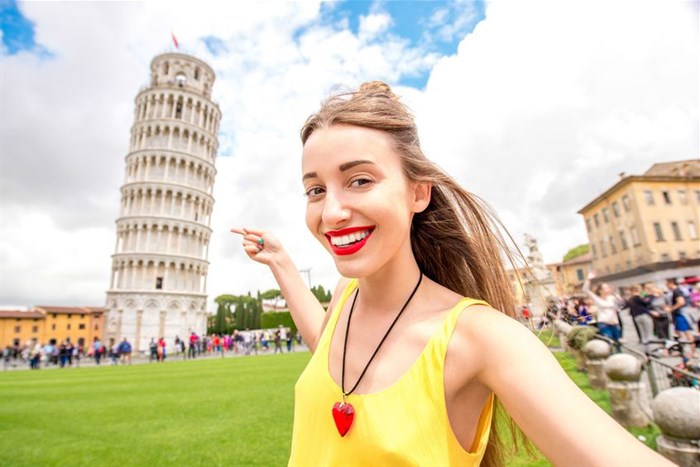
‘Selfie gaze’ tourists
These “selfie gaze” tourists see and experience the destination largely through their cameras and the comments and feedback that they receive to their posts.
In this sense, their satisfaction does not depend on the quality of the destination and experience, but on how well they manage impressions and attract “likes” and positive comments.
The perception that “everyone is watching me” has also changed the way people consume places and what they see and how they behave at a destination. This is because online profiles and posts have to be carefully managed by tourists to highlight positive attributes, socially desirous experiences and present a more idealised self.
Selfie gaze tourists do not only participate in touristic photography – they also artificially create it. Such tourists engage in the performance of various intimate relations (hugging family members) and facial expressions to externalise emotions (duck face).
Thus, gone are the days that destinations had control of their image making and communication. Once used as a travel memory, social media has converted personal photography to a significant source of travel inspiration and the most popular way of online communication, self-expression and identity formation.
The Insta-tourist
Instagram hosts more than 220 million photographs hashtagged with #selfie and more than 330 million hashtagged with #me. People go to such trouble to get the perfect picture of themselves — creating at least a moment that is artificial – in their quest for an image of authenticity.
Tourists get killed, get condemned by priests or arrested by police for insulting local culture and people, or disturb local nature.
EU countries have banned selfies at major landmarks such as Eiffel Tower, while attractions and museums ban the use of selfie sticks for the physical protection of other tourists.
In the quest for self-promotion and the search of an idealised tourism experience, my research shows how tourists share fake and unrealistic information. This could include “checking-in” to places they haven’t been or pretending to be happy despite staying in terrible conditions.
Although this deviant online behaviour biases and dilutes others in their travel decisions, tourists continue doing it believing it doesn’t harm anyone. But it can distort the real travel experience and give people false expectations about destinations.
Influencer marketing
Tourism marketers spend more and more of their marketing budget on influencer marketing, a strategy referring to the use of celebrities and online opinion leaders to post favourable content for a brand.
The influencer market has increased from $10 to $15bn in 2017. Over one-third of marketers now spend over $500,000 a year on influencer marketing and $255m are spent per month just for Instagram posts by influencers. Almost half (48%) of recently surveyed marketers expect their influencer marketing budgets to increase in 2017.
Research shows that it is not age, but the dark triad of personality traits – narcissism, Machiavellianism and psychopathy that push people to pursue selfie glory regardless of the result.
Selfie-gaze tourism also lead to conspicuous consumption in which tourists travel to destinations and perform experiences in front of the camera to display economic power and attain or maintain social status.
Deeper tourism education needed
Obviously, it’s not useful to rail against basic human needs or deny the functional benefits of technology. But what we need instead is a serious education of tourists and citizens for a mindful use of social media before and while travelling.
 This is an area of research that urgently needs to be explored to ensure technology use does not negatively influence travellers psychological, mental, emotional or even physical well-being.
This is an area of research that urgently needs to be explored to ensure technology use does not negatively influence travellers psychological, mental, emotional or even physical well-being.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.